02.
So, What Exactly IS Data Analytics?
Data Analytics Explained
You’ve heard the term data analytics before, and maybe you even have some experience with data already and are familiar with it. However, this term gets thrown around a lot and it’s not always used the same way.
Let’s take a look at the definition from CIO.com:
“Data analytics is a discipline focused on extracting insights from data, including the analysis, collection, organization, and storage of data, as well as the tools and techniques used to do so.”
Data analytics is often presented as a sub-discipline of Computer Science. In real-world application, think of data analytics as the intersection of IT, statistics, and business. The best analysts combine these fields in order to increase efficiency and improve business performance by discovering patterns in data that help the organization succeed.
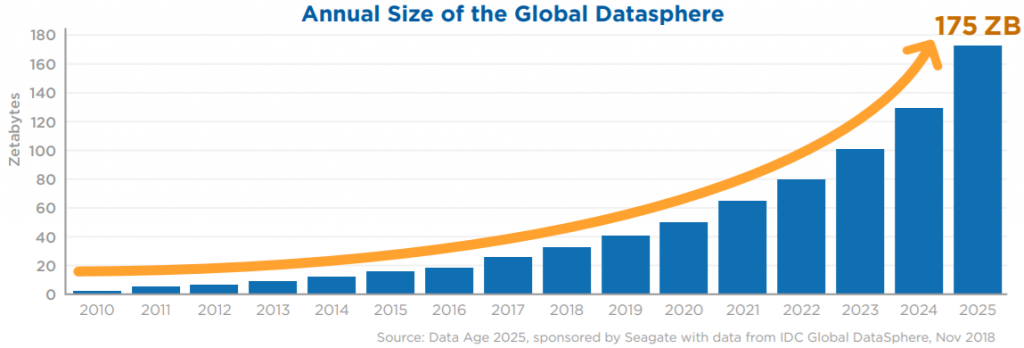
With modern technology like computers, smartphones, apps, social media, and powerful software, you can imagine the pure volume of data that exists in the world.
In fact, the International Data Corporation (IDC) predicts that the collective sum of the world’s data will grow from 33 zettabytes this year to a 175ZB by 2025, for a compounded annual growth rate of 61 percent.
Furthermore, according to Gartner research, "the average financial impact of poor data quality in organizations is $9.7 million per year."
IBM also discovered that in the US alone, businesses lose $3.1 trillion annually due to poor data quality.
So, can you see how important data scientists are to helping stream efficiency, increase profitability, and contribute to the organization’s success?
What is a Data Analyst?
The work of a data analyst can be grouped into four main categories: data mining, data management, statistical analysis, and data presentation. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
Data Mining
Just like it sounds, data mining involves extracting data from data sources that are typically unstructured (meaning they're more qualitative), such as written text, complex databases, or simply raw data. The first step is to combine all of that data and convert it into a format that’s manageable and useful so that it can be analyzed.

Data Management
Also known as data warehousing, data management is the process of creating databases that allows easy access to the results of data mining. Typically, this involved creating and managing Structured Query Language (SQL) databases.

Statistical Analysis
This is the step of the process in which analysts create insights from the data. With a combination of statistics and machine learning, data scientists analyze models that reveal trends and patterns in the data. From there, those models can be applied to make predictions and inform decision making.

Data Presentation
Data is largely useless if you can’t present it in a way that makes a convincing argument or at least in a way that people without data backgrounds can understand. Sharing insights with stakeholders is important, and using compelling visualizations to help tell the story is absolutely essential.

